Cyber Threats: Actionable Strategies for 2023

The last year has dramatically underscored the impact of rapidly evolving cyber threats – and information security vulnerabilities – in healthcare. Many health delivery organizations still lack even basic visibility into the medical devices (and other connected devices) that they own. Repeat ransomware attacks aimed at hospitals and health systems are increasingly common. Cyber insurance premiums are rising, and cyber policies now have more coverage exclusions. Meanwhile, new attack vectors and vulnerabilities continue to emerge (i.e., APIs) that hospitals and health systems need to be prepared to address.
Repeat Ransomware Attacks Common
43% of respondents said their organization has experienced “one or more ransomware attacks” – and of that group, 76% said they have experienced three or more ransomware attacks in just the last 24 months.
Source: “The Insecurity of Connected Devices in Healthcare 2022,” Ponemon Institute / Cynerio, Aug 2022
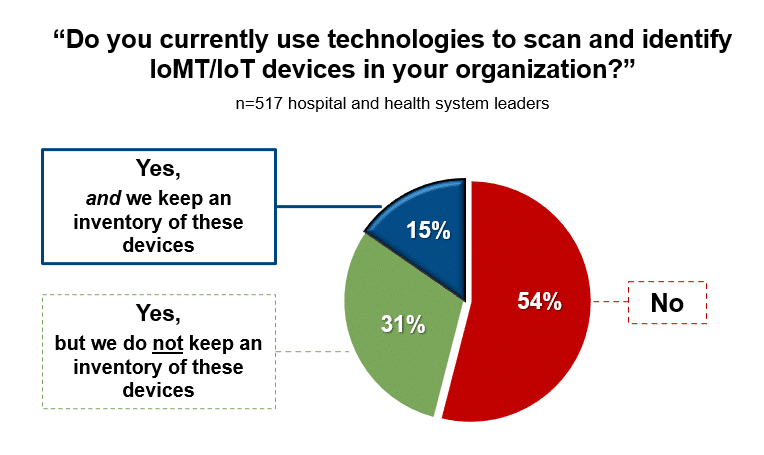
Only 15% of surveyed health delivery organizations use technologies to scan and identify IoMT/IoT devices and keep an inventory of those devices.
The reality is that cybercriminals are not just trying to infiltrate hospitals and health systems directly; they are also gaining access to health delivery organizations by targeting providers’ business and trading partners. Complicating matters is the increasing consolidation among third-party IT vendors, inconsistent due diligence from third-party vendors in vetting their own vulnerabilities, and misconceptions among vendors and providers alike about what is ultimately still a shared cloud security model.

Actionable Strategies
-
Conduct regular, comprehensive, and objective evaluations of the organization’s information security program to assess overall maturity and the measures needed to effectively prepare for – and respond to – emerging cyber threats.
-
Evaluate business partners, third-party vendors, and device makers; hold them accountable to the same standards and align with those that have appropriate security controls.
-
Conduct a business impact analysis to determine an intolerable amount of risk for the organization – and align IT security spending accordingly.
-
Engage and retain the right staff to enable and support security posture.
-
Ensure key decision makers have access to comprehensive, real-time information on enterprise risk posture (inclusive of an exhaustive device inventory) that can fuel proactive, analytics-driven processes and provide an accurate depiction of overall risk.

























